

If the fracture extends only into an unerupted third molar area, and there is no break in the surface mucosa, such fractures are considered closed.Ĭlosed fractures may not require antibiotics before surgery but may be treated with prophylactic antibiotics in the perioperative period. The surgeon can either remove the offending tooth or leave it in place if it is thought not to compromise the result of fracture treatment.Īny fracture that involves the periodontal ligament space of an erupted tooth should be considered an open (contaminated) fracture, requiring administration of systemic antibiotics, at least until the fracture has been reduced and stabilized.īecause many fractures through the angle communicate with either the erupted third or second molars, most angle fractures are open. However, any fracture involving the jaw's dentate areas can involve erupted teeth in the fracture line. infection rates of open fracture depend on zone of injury, periosteal stripping and delay in treatment. Commonly, there are impacted wisdom teeth associated with mandibular angle fractures. ideal time of soft tissue coverage controversial, but most centers perform within 5-7 days. For additional information visit Linking to and Using Content from MedlinePlus.A common problem in managing mandibular fractures involves dealing with teeth in the line of fracture. Open fractures make it easy for bacteria and other contaminants to invade.
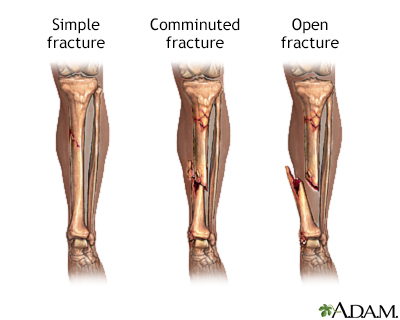
OPEN VS CLOSED FRACTURE SKIN
A closed fracture means the skin was unharmed and remains intact. You have an open fracture when the bone breaks through the skin or you suffer a deep wound that exposes the bone. Closed reduction should be limited to nondisplaced or minimally displaced fractures. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited without authorization. closed fractures All types of fractures are either open or closed. Open vs Closed Reduction and the Role of Capsulotomy Given the importance of an anatomic reduction, there should be a very low threshold for open reduction when treating FNF in a young patient. 1 Egypt was also the site of the earliest examples of active fracture care (e.g., splints) on an unhealed femur fracture. 1 The earliest documentation of fracture care was in the Egyptian Edwin Smith papyrus, circa 1600 b.c. Links to other sites are provided for information only - they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. Through the 20th century, the nonsurgical treatment of closed fractures (i.e., when bone is broken, but skin intact) have been the standard of care. A licensed physician should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. Although the relative risk of development of ACS was lower among patients with open fractures. Open fractures, sometimes called compound fractures, can occur when there is a small cut to the skin that communicates to a fracture, or they can occur with severe soft-tissue injuries that threaten the survival of the limb. This site complies with the HONcode standard for trustworthy health information: verify here. In this study we did not find a significant relationship between type of fracture (open vs closed), anatomical site of tibia fracture, type of trauma, fixation method, or mechanism of injury and development of ACS. Through the 20th century, the nonsurgical treatment of closed fractures (i.e., when bone is broken, but skin intact) have been the standard of care. Open fractures are injuries to the bone that occur when a broken bone is exposed outside the body. Fractures may occur lengthwise, crosswise, or in multiple pieces. If a fracture line is not evident initially (eg. Learn more about A.D.A.M.'s editorial policy editorial process and privacy policy. Although generally rigid, bones can weaken over time and become more susceptible to fracturing. A hematoma forms at the fracture site, and a small amount of bone in the distal fracture fragments is resorbed. is among the first to achieve this important distinction for online health information and services. Reasons for considering open reduction include: To reduce the risk of avascular necrosis To avoid/prevent the risk of delayed union/nonunion To avoid/prevent the risk of malunion 2. follows rigorous standards of quality and accountability. Introduction Open reduction is used for the majority of pediatric femoral neck fractures. Most often, this wound is caused by a fragment of bone breaking through the skin at the moment of the injury. is accredited by URAC, for Health Content Provider (URAC's accreditation program is an independent audit to verify that A.D.A.M. Diseases & Conditions Open Fractures An open fracture, also called a compound fracture, is a fracture in which there is an open wound or break in the skin near the site of the broken bone.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
